SDRAM and its types
Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory is the full form of SDRAM. It synchronized the memory speed with the CPU clock speed so that the memory controller knows the CPU clock cycle. It also keeps data buses continuously busy. In this way, the CPU can execute more instructions at once. It is faster than DRAM.
Types Of SDRAM
SDRAM technology undergoes a huge amount of development. As a result, a number of memories were introduced in each generation with improved performance over the previous generation.
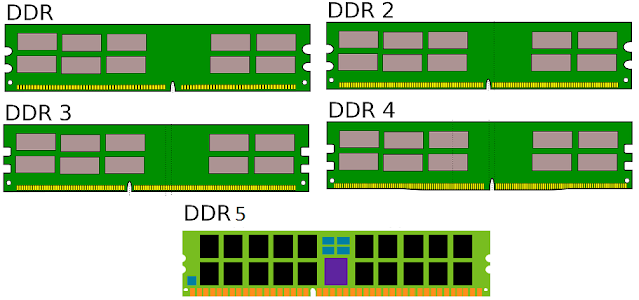
DDR SDRAM
The full form of DDR SDRAM is Double Data Rate SDRAM. It is also known as DDR1 SDRAM. It was launched in 2000 but used in 2002. It provides double data transfer speed which means a greater speed than a traditional type of SDRAM memory. This is achieved by transferring data twice per cycle. The number of contact pins in DDR1:184-pin (DIMM), 200-pin (SO-DIMM), and 172-pin (micro DIMM).
DDR2-SDRAM is a high-performance synchronous dynamic RAM. It was first introduced in 2003. It offers new features, greater bandwidth, and lesser power consumption than DDR SRAM. The number of contact pins in DDR2: 240-pin (DIMM), 200-pin (SO-DIMM), and 214-pin (micro DIMM).
DDR3 SDRAM
DDR3 RAM is similar to DDR2 RAM, but uses roughly 30% less power and can transfer data twice as fast. It was introduced in 2007. It provides further improvements in overall performance and speed. The number of contact pins in DDR3: 240 pins (DIMM), 204 pins (SO-DIMM), and 214 pins (micro DIMM).
DDR4 SDRAM
DDR4 SDRAM was the next generation of DDR SDRAM. It was introduced in late 2014. Faster speeds and increased memory bandwidth allow DDR4 SDRAM to keep up with modern processors, including multi-core CPUs. The number of contact pins in DDR4: 288-pin (DIMM), 256-pin (SO-DIMM). DDR4 micro DIMMs no longer exist.
DDR5 SDRAM
The development of SDRAM technology is moving forwards and the next generation of SDRAM is DDR5. It was released on 14 July 2020. DDR5 reduces power consumption while doubling bandwidth and capacity.






Comments
Post a Comment